1D Convolutional
Below is a basic example of an 1D convolutional neural network implemented with PyTorch and Tensorflow 2. As an example, we build a dataset of 1D sinus signals, the goal of the network is to recover the frequency of that signal.
Below is NOT the architecture of the network, it’s a figure that helps understanding what means the terms “stride”, “padding”, “max pooling”, etc:
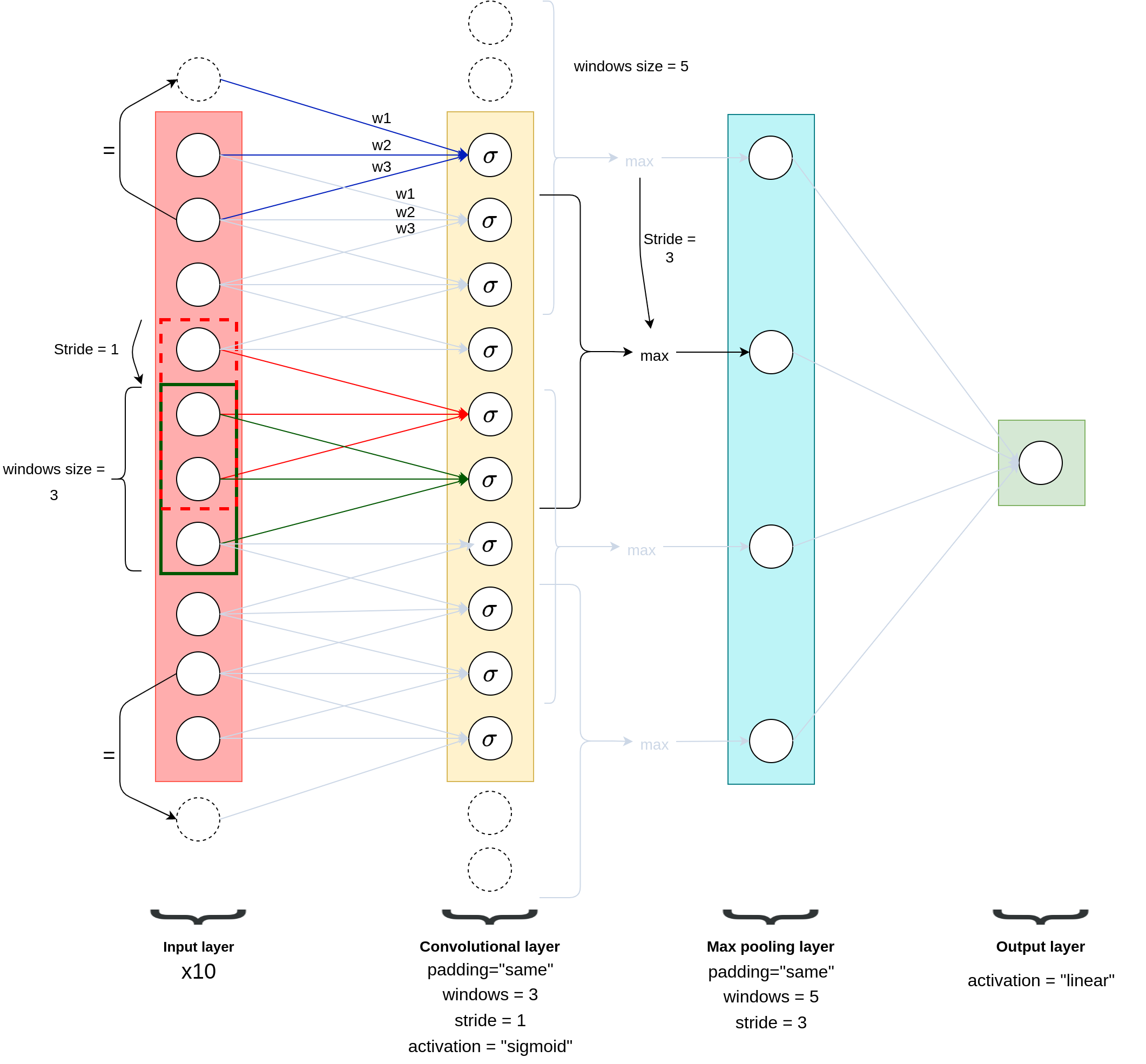
Below is the code to create the dataset:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
# Creating the dataset
###############################################################################
# x = random sinusoidal signal in between 1 and 100hz
# y = frequency of the signals
NbPoints = 1000
fmin_hz = 1
fmax_hz = 100
fs_hz = 800.0
f_list = []
snr_list = []
x_list = []
for k in range(0, 20000):
# Random frequency and phase
frequency = np.random.rand(1) * (fmax_hz - fmin_hz) + fmin_hz
phase = np.random.rand(1) * np.pi * 2
# Signal
x_temp = np.sin(2 * np.pi * frequency * np.arange(0, NbPoints) * (1. / fs_hz) + phase)
# Adding noise
signal_power_dB = 10.0 * np.log10(np.sum(np.power(x_temp, 2)) / len(x_temp))
snr_db = np.random.randn(1) * 3 + 15
noise_power = np.power(10.0, (signal_power_dB - snr_db) / 10.0)
noise = np.random.normal(loc=0, scale=np.sqrt(noise_power), size=NbPoints)
x_temp += noise
# Adding the new data to the array
f_list.append(frequency)
snr_list.append(snr_db)
x_list.append(x_temp)
X = np.array(x_list)
y = np.array(f_list).reshape((len(f_list), 1))
# Plotting a sample of one input
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 4), tight_layout=True)
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax1.plot(np.arange(1000) * 1/fs_hz, X[0], '-x')
ax1.grid()
ax1.set_xlabel("Time [s]")
ax1.set_ylabel("Amplitude")
ax1.set_title("Frequency: %.1f Hz, SNR: %.1f dB" % (f_list[0], snr_list[0]))
fig.savefig("input_sample.png", dpi=200)
# Pre-Processing
###############################################################################
# Splitting the dataset into the training set and test set
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2)
# Features scaling
sc_y = StandardScaler()
y_train = sc_y.fit_transform(y_train.reshape(-1, 1))
y_test = sc_y.transform(y_test.reshape(-1, 1))
# Learning Parameters
###############################################################################
learning_rate = 0.04
nb_epochs = 50
batch_size = 500 # Better practice to take a multiple a number so that batch_size % X_train.shape[0] = 0
p_dropout = 0.25 # probability to be zeroed
# Number of iterations = nb_epochs * X_train.shape[0] / batch_size
Example of an input:
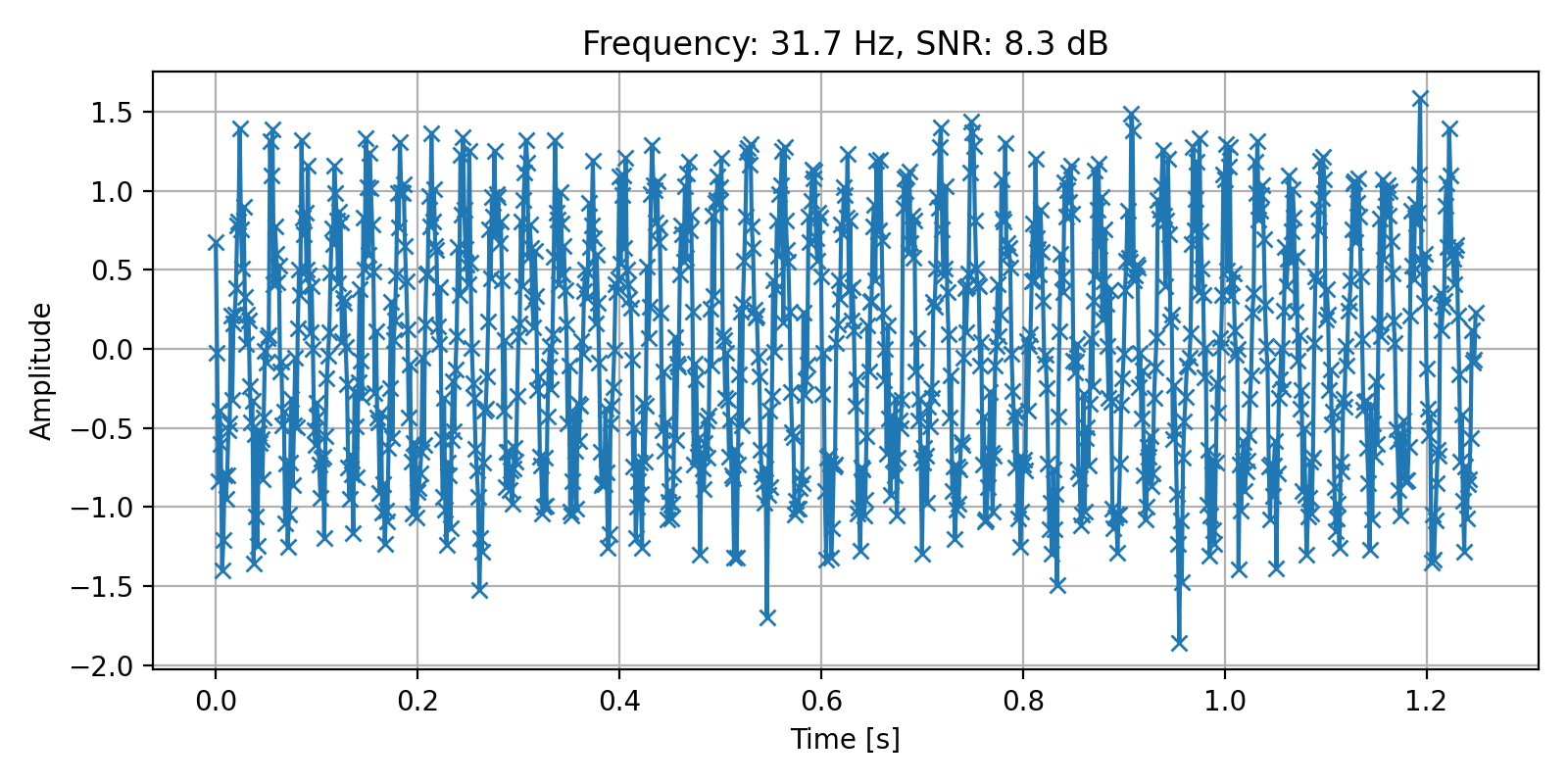
Using PyTorch
Version of Pytorch used: 1.12.1
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
import math
# Pytorch 1.12.1
# Creating the model
###############################################################################
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
class MLP(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, p_dropout:float):
super(MLP, self).__init__()
self.p_dropout = p_dropout
self.num_input = 1000
self.c11_params = {
"size": 3,
"features": 1,
"stride": 1,
"maxpool_size": 2,
"maxpool_stride": 1
}
self.c12_params = {
"size": 2,
"features": 2,
"stride": 1,
"maxpool_size": 2,
"maxpool_stride": 1
}
self.n_hidden_2 = 100
self.num_output = 1
# Number of neurons for each convolutional layer (after max pooling)
# value padding='SAME'
self.c11_size = math.ceil(math.ceil(self.num_input / self.c11_params["stride"]) / self.c11_params["maxpool_stride"]) * self.c11_params["features"]
self.c12_size = math.ceil(math.ceil(self.num_input / self.c12_params["stride"]) / self.c12_params["maxpool_stride"]) * self.c12_params["features"]
if not (self.c11_params["maxpool_size"] % 2) and (self.num_input % self.c11_params["maxpool_stride"] == 0):
self.c11_size += self.c11_params["features"]
if not (self.c12_params["maxpool_size"] % 2) and (self.num_input % self.c12_params["maxpool_stride"] == 0):
self.c12_size += self.c12_params["features"]
# 1D Convolutional layer
self.c11 = nn.Conv1d(1, self.c11_params["features"], self.c11_params["size"], self.c11_params["stride"], padding="same", padding_mode="reflect")
# 1D Convolutional layer
self.c12 = nn.Conv1d(1, self.c12_params["features"], self.c12_params["size"], self.c12_params["stride"], padding="same", padding_mode="reflect")
# Fully connected layer
self.l2_linear = nn.Linear(self.c11_size + self.c12_size, self.n_hidden_2)
self.out_linear = nn.Linear(self.n_hidden_2, self.num_output)
# Activation functions
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p_dropout)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
pad1 = math.ceil((self.c11_params["maxpool_size"] - 1) / 2)
pad2 = math.ceil((self.c12_params["maxpool_size"] - 1) / 2)
self.mp1 = nn.MaxPool1d(self.c11_params["maxpool_size"], stride=self.c11_params["maxpool_stride"], padding=pad1)
self.mp2 = nn.MaxPool1d(self.c12_params["maxpool_size"], stride=self.c12_params["maxpool_stride"], padding=pad2)
### If you want to initialize weights (not recommended as pytorch is already doing it for you)
# def init_weights(m):
# if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
# torch.nn.init.normal_(m.weight)
# torch.nn.init.normal_(m.bias)
# self.apply(init_weights)
### By default: model parameters are single precision float (float32)
# Input data must match the type of the model
# you can convert the model to double by adding self.double()
def forward(self, x):
x = torch.unsqueeze(x, 1)
c1 = self.mp1(self.c11(x))
c2 = self.mp2(self.c12(x))
l1 = torch.cat((c1.reshape(c1.shape[0], -1), c2.reshape(c2.shape[0], -1)), 1)
l2 = self.dropout(self.sigmoid(self.l2_linear(l1)))
out = self.out_linear(l2)
return out
# Prepare the DataLoader
###############################################################################
class SinusDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x
self.y = y
def __len__(self):
return self.x.shape[0]
def __getitem__(self, ind):
return self.x[ind], self.y[ind]
train_set = SinusDataset(X_train, y_train)
test_set = SinusDataset(X_test, y_test)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_set, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_set, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False)
# Train the model
###############################################################################
model = MLP(p_dropout).to(device)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
loss = nn.MSELoss() # nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
model.train() # Set the model in training mode
for num_epoch in range(nb_epochs):
losses = []
for batch_num, (x, y) in enumerate(train_loader):
optimizer.zero_grad()
x = x.to(device).float()
y = y.to(device).float()
output = model(x)
batch_loss = loss(output, y)
batch_loss.backward()
losses.append(batch_loss.item())
optimizer.step()
if batch_num % 10 == 0:
print(f"\tEpoch {num_epoch: 3d} | Batch {batch_num: 4d} | Loss {batch_loss.item():9.5f}")
model.eval() # Set the model in evaluation mode (ignoring dropouts)
losses_test = []
for xt, yt in test_loader:
xt = xt.to(device).float()
yt = yt.to(device).float()
output = model(xt)
batch_loss = loss(output, yt)
losses_test.append(batch_loss.item())
print(f"Epoch {num_epoch: 3d} | Loss Training {sum(losses)/len(losses):9.5f} | Loss Testing {sum(losses_test)/len(losses_test):9.5f}")
model.train()
print("Optimization Finished!")
# Printing and plotting the results
###############################################################################
model.eval()
y_pred = []
for xt, _ in test_loader:
xt = xt.to(device).float()
output = model(xt)
output = output.cpu().detach().numpy().flatten().tolist()
y_pred += output
# Predicting the test set results
f_target = sc_y.inverse_transform(np.array(y_test).reshape(-1, 1)).reshape(len(y_test))
f_prediction = sc_y.inverse_transform(np.array(y_pred).reshape(-1, 1)).reshape(len(y_pred))
# Mean Error
mean_error = np.mean(np.abs(f_target - f_prediction))
# Std Error
std_error = np.std(np.abs(f_target - f_prediction))
print("Error => Mean: ", mean_error, " Hz; Std: ", std_error, " Hz")
# Plotting the results
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4), tight_layout=True)
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax1.plot(f_target, f_prediction, 'x', label="Estimations")
ax1.plot([fmin_hz, fmax_hz], [fmin_hz, fmax_hz], color='r', linewidth=2.0, label="Ideal results")
ax1.grid()
ax1.legend()
ax1.set_xlabel("Frequency to retrieve [Hz]")
ax1.set_ylabel("Frequency estimated [Hz]")
fig.savefig("CONV_Predictions_pt.png", dpi=200)
Output:
Epoch 48 | Batch 0 | Loss 0.04520
Epoch 48 | Batch 10 | Loss 0.04244
Epoch 48 | Batch 20 | Loss 0.04208
Epoch 48 | Batch 30 | Loss 0.04039
Epoch 48 | Loss Training 0.04514 | Loss Testing 0.01751
Epoch 49 | Batch 0 | Loss 0.04864
Epoch 49 | Batch 10 | Loss 0.04190
Epoch 49 | Batch 20 | Loss 0.03814
Epoch 49 | Batch 30 | Loss 0.04388
Epoch 49 | Loss Training 0.04587 | Loss Testing 0.01277
Optimization Finished!
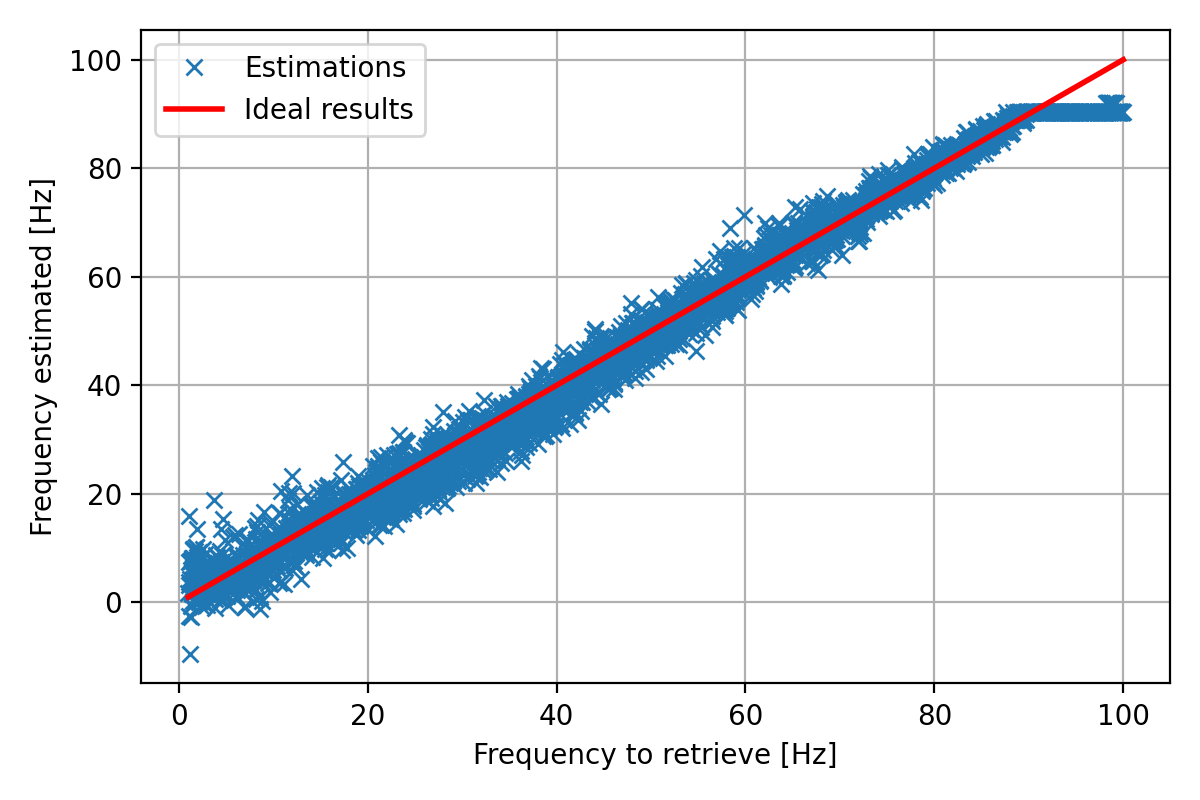
Error => Mean: 2.4226592277440573 Hz; Std: 2.1281719568276327 Hz
Results on the test dataset:
Using Tensorflow
Version of Tensorflow used: 2.9.0
import numpy as np
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
import math
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Creating the model
###############################################################################
class MLP():
def __init__(self, dropout_rate):
self.dropout_rate = dropout_rate
self.num_input = 1000
self.c11_params = {
"size": 3,
"features": 1,
"stride": 1,
"maxpool_size": 2,
"maxpool_stride": 1
}
self.c12_params = {
"size": 2,
"features": 2,
"stride": 1,
"maxpool_size": 2,
"maxpool_stride": 1
}
self.n_hidden_2 = 100
self.num_output = 1
# Number of neurons for each convolutional layer (after max pooling)
# value padding='SAME'
self.c11_size = math.ceil(math.ceil(self.num_input / self.c11_params["stride"]) / self.c11_params["maxpool_stride"]) * self.c11_params["features"]
self.c12_size = math.ceil(math.ceil(self.num_input / self.c12_params["stride"]) / self.c12_params["maxpool_stride"]) * self.c12_params["features"]
# Store layers weight & bias
# 1D Convolutional layer
self.w_c11 = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([self.c11_params["size"], 1, self.c11_params["features"]]), trainable=True, dtype=tf.float32)
self.b_c11 = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([self.c11_params["features"]]), trainable=True, dtype=tf.float32)
# 1D Convolutional layer
self.w_c12 = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([self.c12_params["size"], 1, self.c12_params["features"]]), trainable=True, dtype=tf.float32)
self.b_c12 = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([self.c12_params["features"]]), trainable=True, dtype=tf.float32)
# fully connected layer
self.w_h2 = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([self.c11_size + self.c12_size, self.n_hidden_2]), trainable=True, dtype=tf.float32)
self.b_h2 = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([self.n_hidden_2]), trainable=True, dtype=tf.float32)
# 1 output
self.w_out = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([self.n_hidden_2, self.num_output]), trainable=True, dtype=tf.float32)
self.b_out = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([self.num_output]), trainable=True, dtype=tf.float32)
self.params = [ self.w_c11, self.b_c11,
self.w_c12, self.b_c12,
self.w_h2, self.b_h2,
self.w_out, self.b_out]
def parameters(self):
return self.params
def forward(self, x):
x = tf.reshape(x, shape=[-1, self.num_input, 1])
# Convolutional layer 1
c11 = tf.nn.conv1d(x, self.w_c11, stride=self.c11_params["stride"], padding='SAME')
c11 = tf.nn.bias_add(c11, self.b_c11)
c11 = tf.nn.max_pool1d(c11, ksize=self.c11_params["maxpool_size"], strides=self.c11_params["maxpool_stride"], padding='SAME')
# Convolutional layer 2
c12 = tf.nn.conv1d(x, self.w_c12, stride=self.c12_params["stride"], padding='SAME')
c12 = tf.nn.bias_add(c12, self.b_c12)
c12 = tf.nn.max_pool1d(c12, ksize=self.c12_params["maxpool_size"], strides=self.c12_params["maxpool_stride"], padding='SAME')
# Fully connected layer
c1 = tf.reshape(c11, [-1, self.c11_size])
c2 = tf.reshape(c12, [-1, self.c12_size])
c = tf.concat([c1, c2], axis=1)
layer_2 = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(tf.matmul(c, self.w_h2), self.b_h2))
do2 = tf.nn.dropout(layer_2, rate=self.dropout_rate)
# Output fully connected layer with a neuron
out_layer = tf.matmul(do2, self.w_out) + self.b_out
return out_layer
# Train the model
###############################################################################
model = MLP(p_dropout)
optimizer = tf.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=learning_rate)
def loss(y_pred, y_true):
return tf.reduce_mean(tf.pow(y_pred - y_true, 2))
for num_epoch in range(nb_epochs):
X_train, y_train = shuffle(X_train, y_train)
for batch_num in range(0, int(np.ceil(X_train.shape[0] / batch_size))):
batch_x = X_train[batch_num * batch_size: (batch_num + 1) * batch_size, :]
batch_y = y_train[batch_num * batch_size: (batch_num + 1) * batch_size, :]
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
batch_loss = loss(model.forward(batch_x.astype(np.float32)), batch_y.astype(np.float32))
grads = tape.gradient(batch_loss, model.parameters())
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, model.parameters()))
if batch_num % 10 == 0:
print(f"\tEpoch {num_epoch: 3d} | Batch {batch_num: 4d} | Loss {tf.reduce_mean(batch_loss):9.5f}")
train_loss = loss(model.forward(X_train.astype(np.float32)), y_train.astype(np.float32))
test_loss = loss(model.forward(X_test.astype(np.float32)), y_test.astype(np.float32))
print(f"Epoch {num_epoch: 3d} | Loss Training {tf.reduce_mean(train_loss):9.5f} | Loss Testing {tf.reduce_mean(test_loss):9.5f}")
print("Optimization Finished!")
# Printing and plotting the results
###############################################################################
y_pred = model.forward(X_test.astype(np.float32))
y_pred = y_pred.numpy().flatten()
# Predicting the test set results
f_target = sc_y.inverse_transform(np.array(y_test).reshape(-1, 1)).reshape(len(y_test))
f_prediction = sc_y.inverse_transform(np.array(y_pred).reshape(-1, 1)).reshape(len(y_pred))
# Mean Error
mean_error = np.mean(np.abs(f_target - f_prediction))
# Std Error
std_error = np.std(np.abs(f_target - f_prediction))
print("Error => Mean: ", mean_error, " Hz; Std: ", std_error, " Hz")
# Plotting the results
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4), tight_layout=True)
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax1.plot(f_target, f_prediction, 'x', label="Estimations")
ax1.plot([fmin_hz, fmax_hz], [fmin_hz, fmax_hz], color='r', linewidth=2.0, label="Ideal results")
ax1.grid()
ax1.legend()
ax1.set_xlabel("Frequency to retrieve [Hz]")
ax1.set_ylabel("Frequency estimated [Hz]")
fig.savefig("CONV_Predictions_tf.png", dpi=200)
Output:
Epoch 48 | Batch 0 | Loss 0.06187
Epoch 48 | Batch 10 | Loss 0.06818
Epoch 48 | Batch 20 | Loss 0.06472
Epoch 48 | Batch 30 | Loss 0.06478
Epoch 48 | Loss Training 0.06278 | Loss Testing 0.07762
Epoch 49 | Batch 0 | Loss 0.05829
Epoch 49 | Batch 10 | Loss 0.06478
Epoch 49 | Batch 20 | Loss 0.06293
Epoch 49 | Batch 30 | Loss 0.06088
Epoch 49 | Loss Training 0.06361 | Loss Testing 0.07427
Optimization Finished!
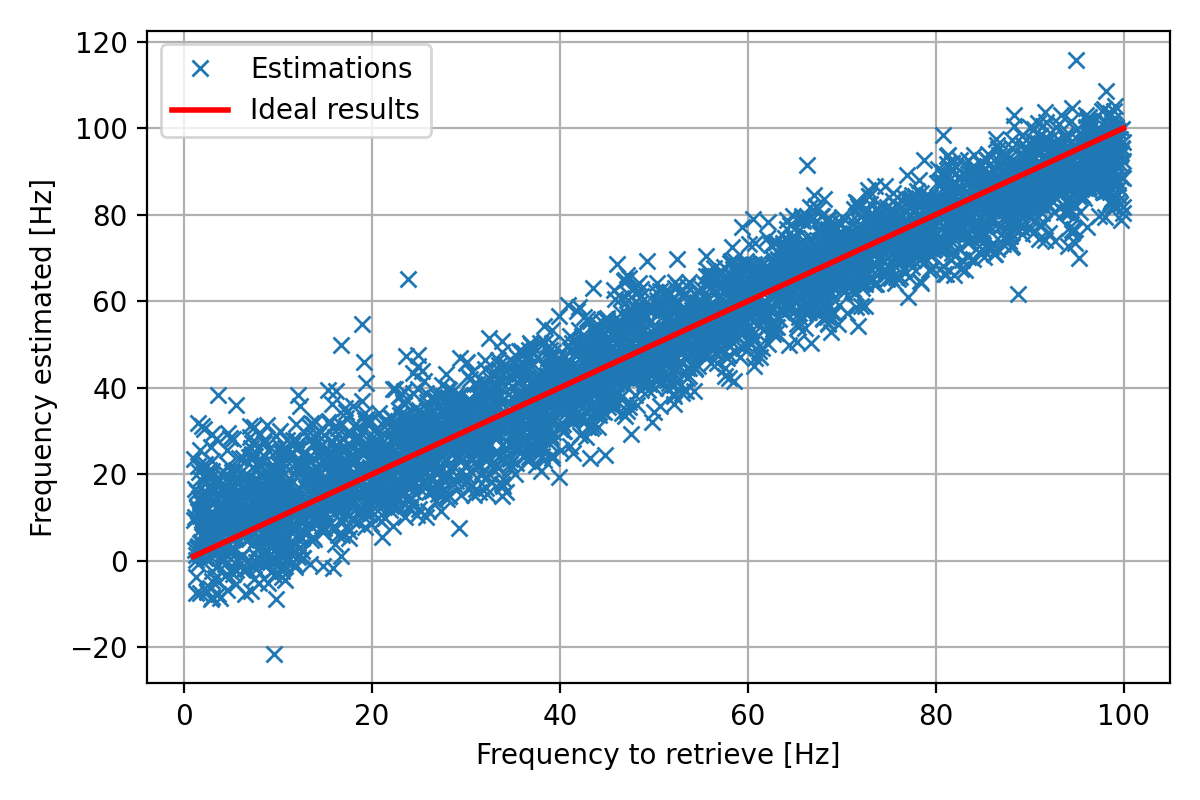
Error => Mean: 5.949109215465254 Hz; Std: 4.7814798241895815 Hz
Results on the test dataset:
Sources:
PyTorch Documentation: https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/index.html
Pytorch: Where to declare layers ? init ? forward ? https://stackoverflow.com/questions/50376463/pytorch-whats-the-difference-between-define-layer-in-init-and-directly-us
PyTorch: Multilayer Perceptron By Xinhe Zhang https://medium.com/deep-learning-study-notes/multi-layer-perceptron-mlp-in-pytorch-21ea46d50e62
PyTorch: Dataset and DataLoader: https://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/basics/data_tutorial.html
Tensorflow Documentation: https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/all_symbols
Tensorflow: Image Classification With TensorFlow 2.0 By Shubham Panchal https://becominghuman.ai/image-classification-with-tensorflow-2-0-without-keras-e6534adddab2
Tensorflow: CNN with Cifar10 https://colab.research.google.com/github/LAVI-USP/Machine-Learning/blob/master/Deep%20Learning/Classifiers/CNN_cifar10_TF2.ipynb
Tensorflow: How to write a Neural Network in Tensorflow from scratch By Hitesh Vaidya https://medium.com/analytics-vidhya/how-to-write-a-neural-network-in-tensorflow-from-scratch-without-using-keras-e056bb143d78